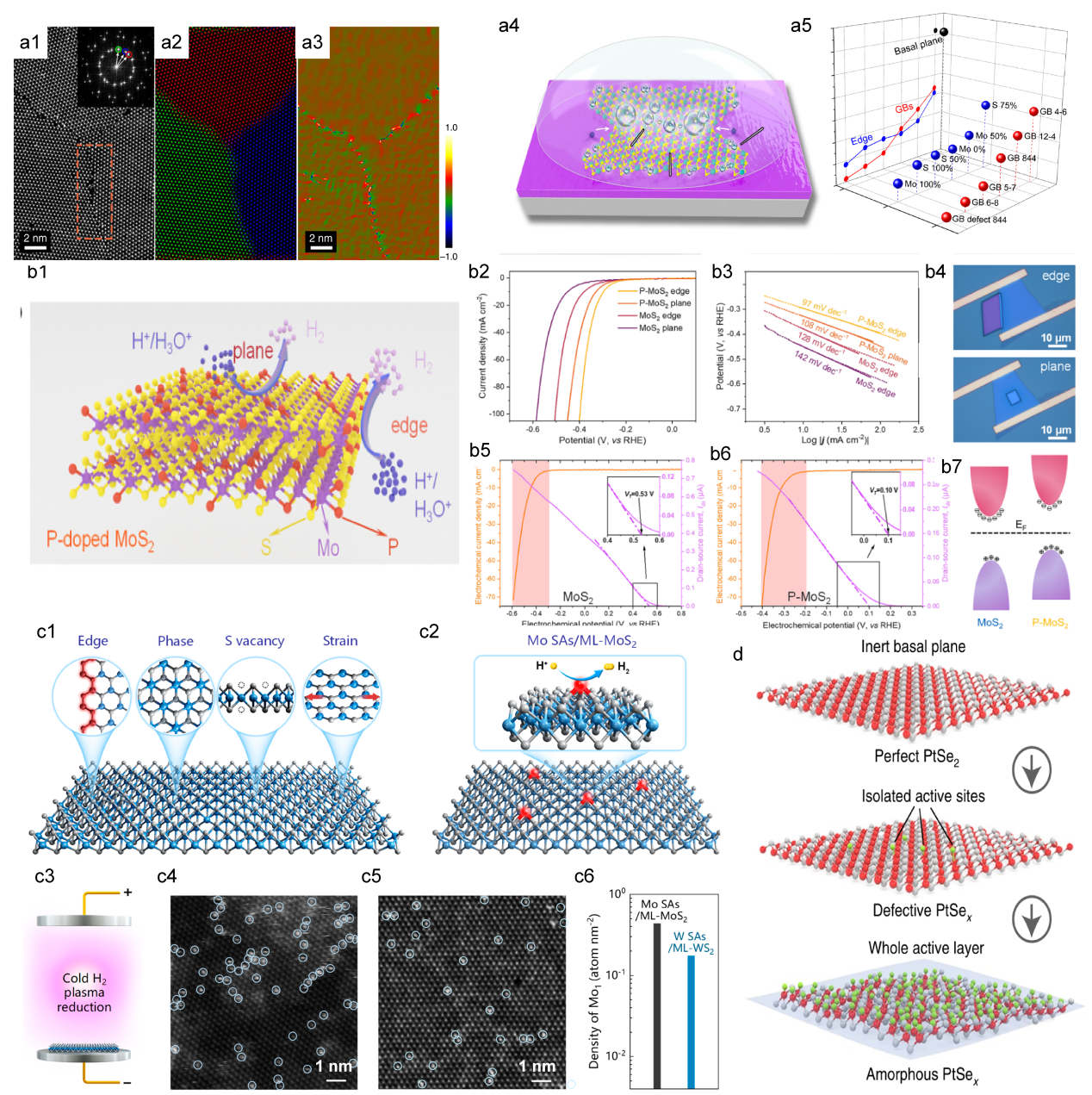
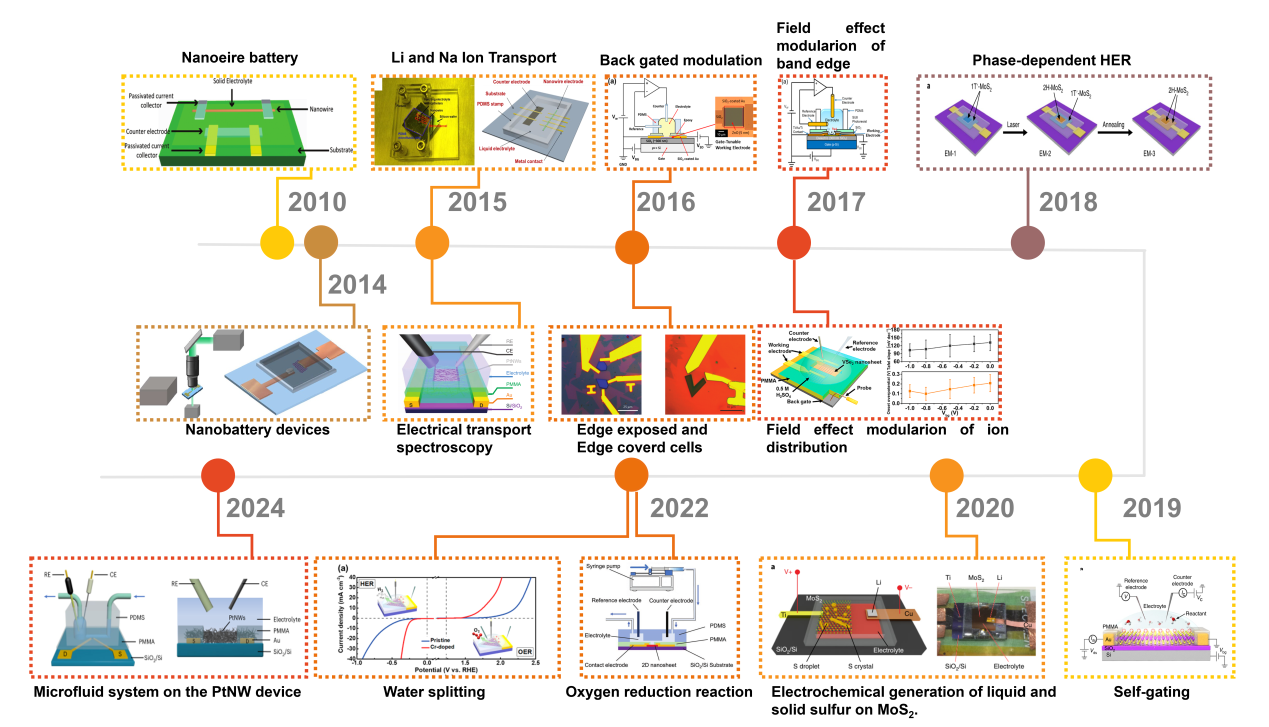
 Figure. 1 Timeline for the on-chip microcell in electrocatalysis.[
Figure. 1 Timeline for the on-chip microcell in electrocatalysis.[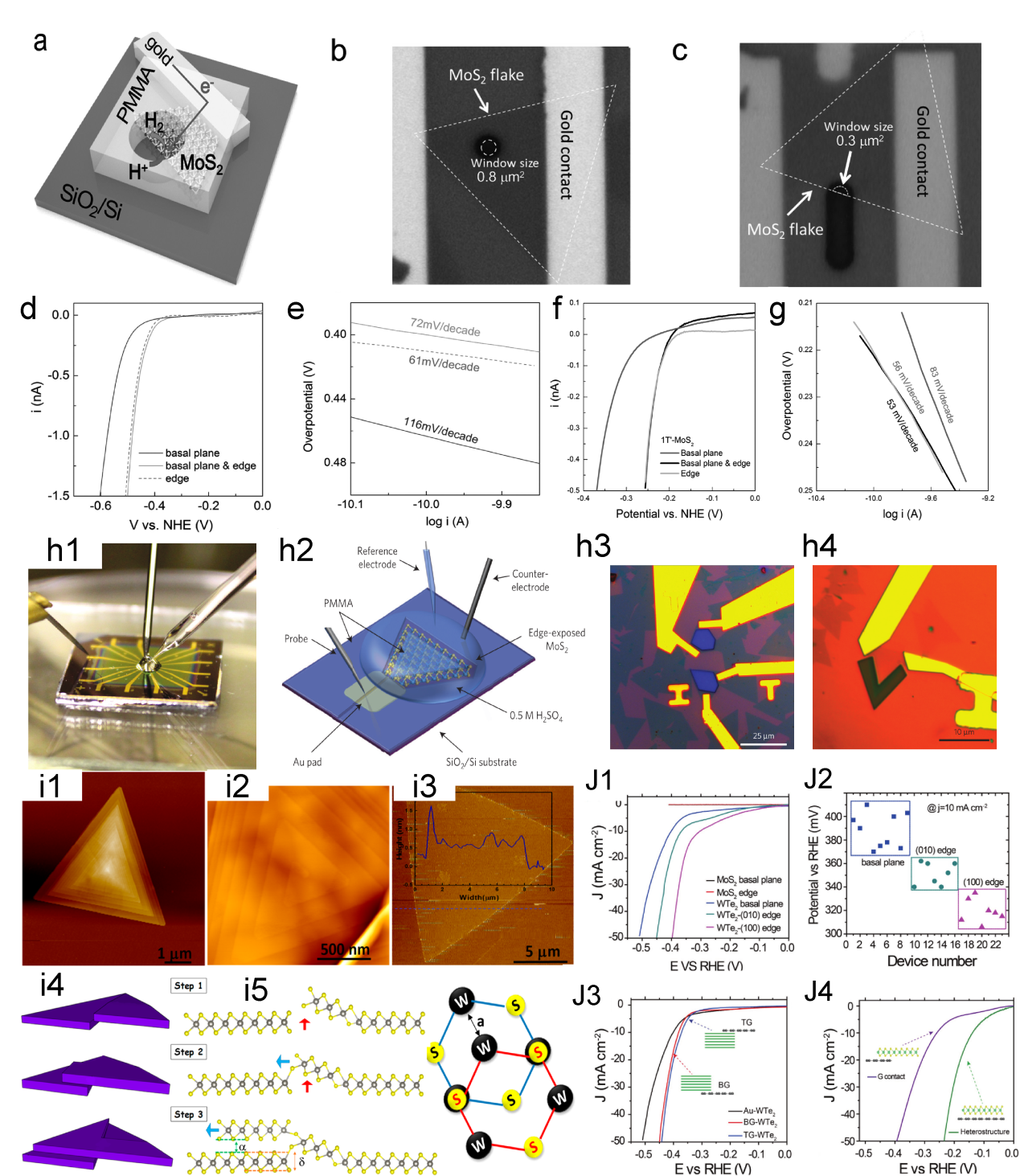 Figure 4. (a) Schematic of the on-chip setup. Optical image of a MoS2 showing the (b) basal and (c) edge planes. (d) LSV and (e) Tafel plots of the MoS2 with basal plane and edge, the electrolyte was argon-purged in 0.5 M H2SO4 and scan rate was set at 10 mV s−1. (f) LSV and (g) Tafel curves of monolayer 1T′-MoS2 basal plane, and edge in HER.[
Figure 4. (a) Schematic of the on-chip setup. Optical image of a MoS2 showing the (b) basal and (c) edge planes. (d) LSV and (e) Tafel plots of the MoS2 with basal plane and edge, the electrolyte was argon-purged in 0.5 M H2SO4 and scan rate was set at 10 mV s−1. (f) LSV and (g) Tafel curves of monolayer 1T′-MoS2 basal plane, and edge in HER.[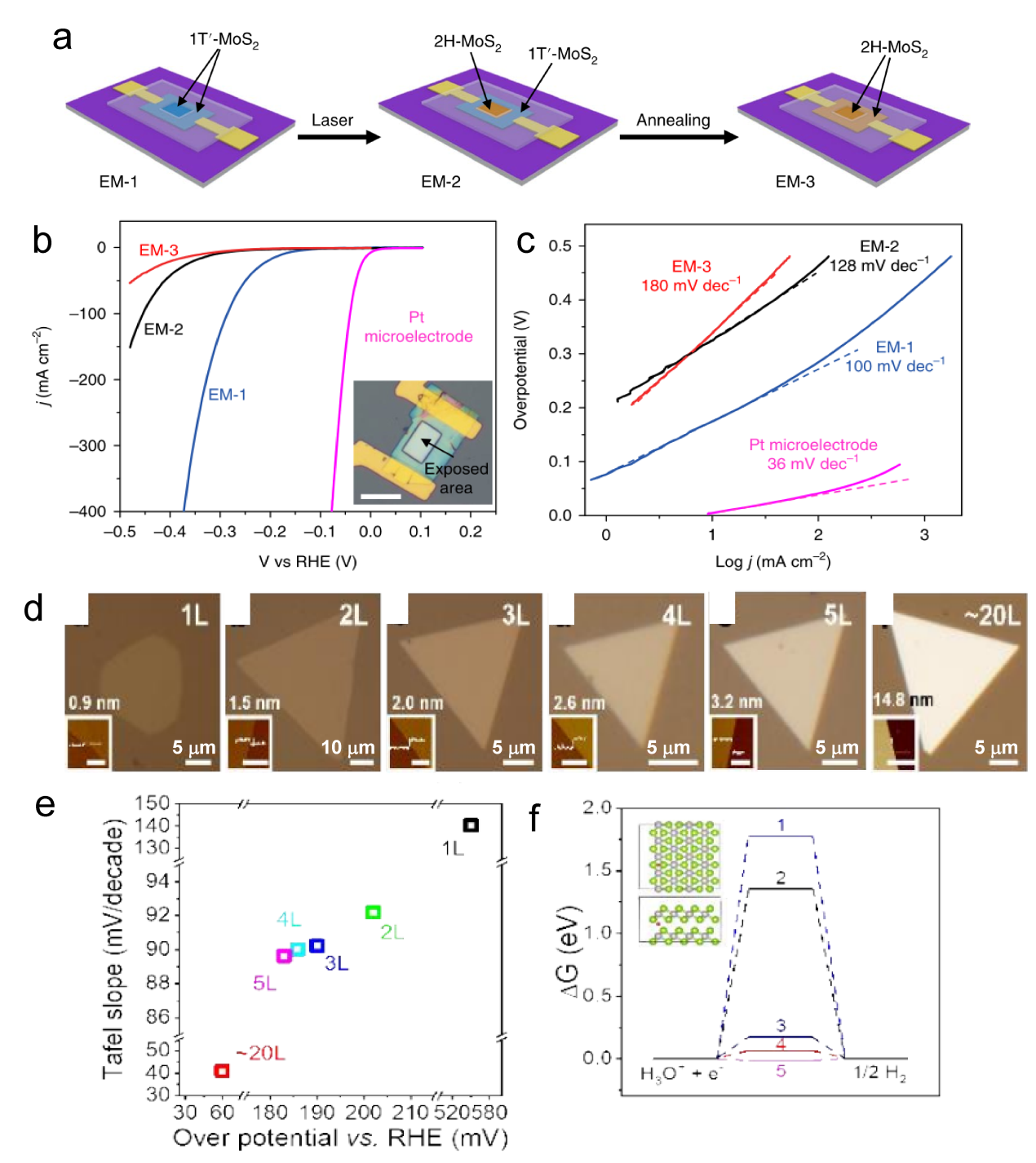 Figure 5. The diagram of fabrication process. (b) The LSV for EM-1, EM-2, and EM-3, with an inset image EM-1, the overpotential of EM-1 and EM-2 is 165 mV and 200 mV, respectively. Scale bar, 20 μm (c) Tafel plots corresponding the (b).[
Figure 5. The diagram of fabrication process. (b) The LSV for EM-1, EM-2, and EM-3, with an inset image EM-1, the overpotential of EM-1 and EM-2 is 165 mV and 200 mV, respectively. Scale bar, 20 μm (c) Tafel plots corresponding the (b).[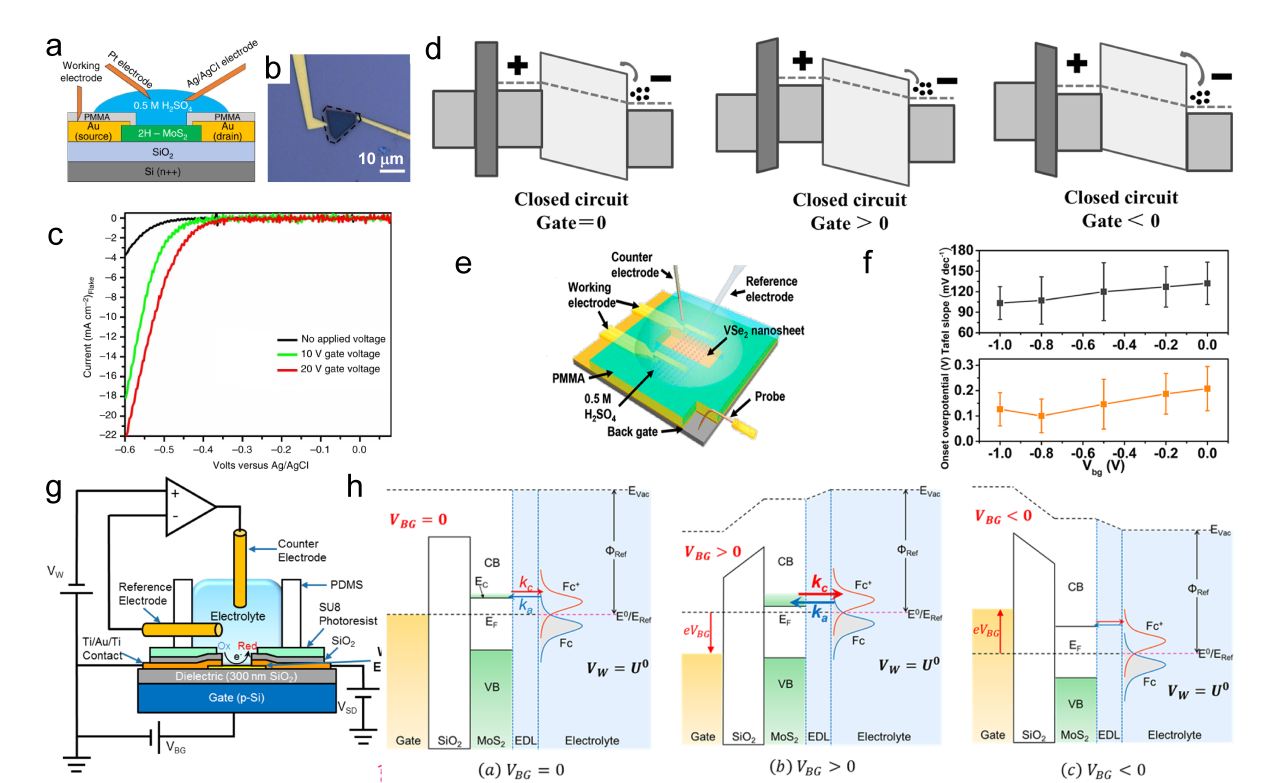 Figure 7. (a) Schematic of the gate-modulation electrochemical device. (b) Optical images of 2H-MoS2 with Au pads. (c) LSV of gate-dependent HER measurements, the green and red curves show the improvement in electrocatalytic activity after applying a positive gate voltage of 10 and 20 V, respectively.[
Figure 7. (a) Schematic of the gate-modulation electrochemical device. (b) Optical images of 2H-MoS2 with Au pads. (c) LSV of gate-dependent HER measurements, the green and red curves show the improvement in electrocatalytic activity after applying a positive gate voltage of 10 and 20 V, respectively.[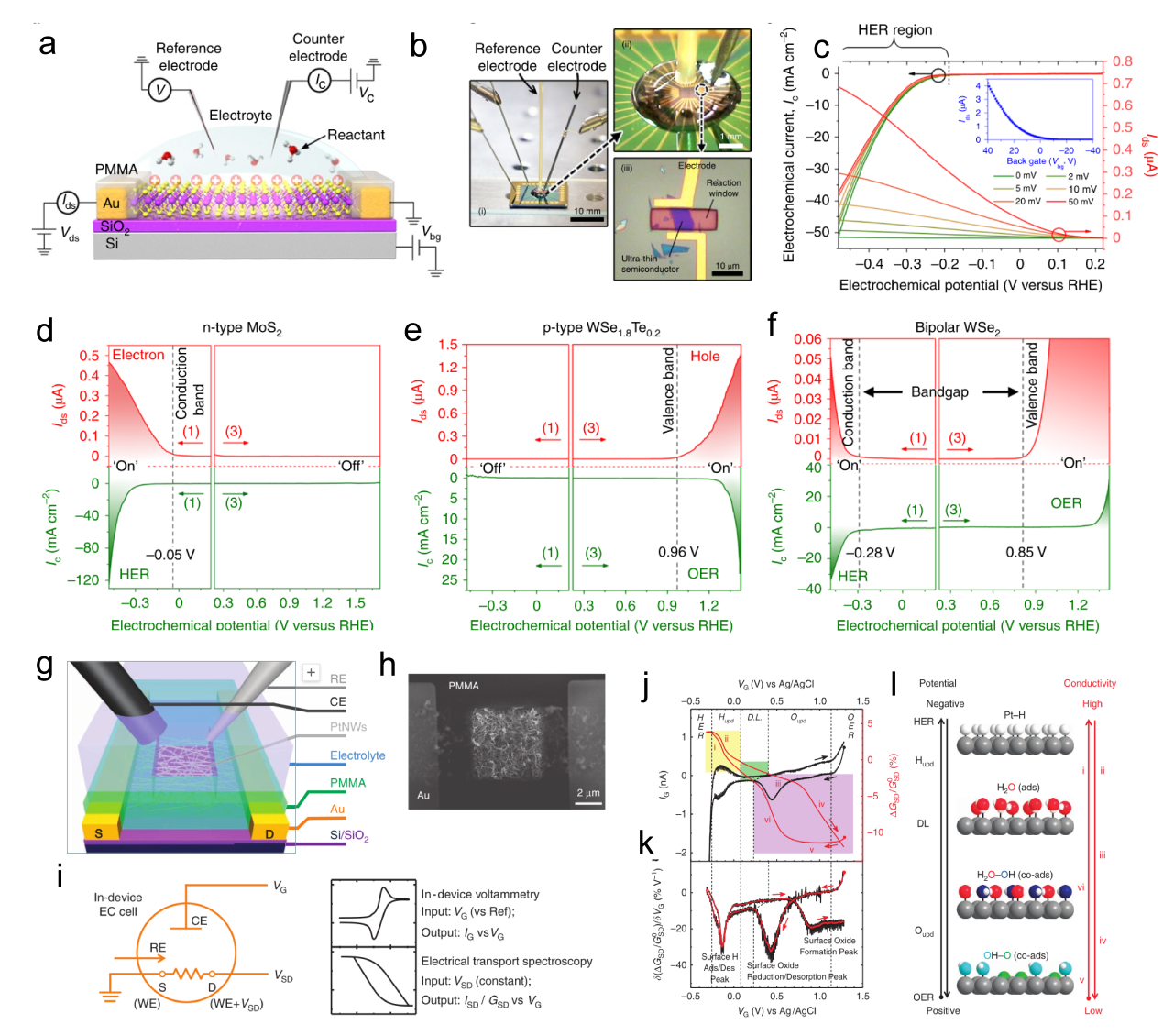 Figure 8. (a) Schematic of the microcell-based in situ electronic/electrochemical measurement. (b) Optical image of the microcell. (c) Typical electrochemical (y axis in black) and electronic (y axis in red) signals of single-layer WS2 during the HER at different bias potentials. Self-gating phenomenon of (d) n-type MoS2, (e) p-type WSe1.8Te0.2, and (f) bipolar WSe2, typically, n-type MoS2 is turned on at a negative electrochemical potential and only delivers the HER, p-type WSe1.8Te0.2 is turned on at a positive electrochemical potential and only delivers the OER, bipolar WSe2 is turned on at both negative and positive electrochemical.[
Figure 8. (a) Schematic of the microcell-based in situ electronic/electrochemical measurement. (b) Optical image of the microcell. (c) Typical electrochemical (y axis in black) and electronic (y axis in red) signals of single-layer WS2 during the HER at different bias potentials. Self-gating phenomenon of (d) n-type MoS2, (e) p-type WSe1.8Te0.2, and (f) bipolar WSe2, typically, n-type MoS2 is turned on at a negative electrochemical potential and only delivers the HER, p-type WSe1.8Te0.2 is turned on at a positive electrochemical potential and only delivers the OER, bipolar WSe2 is turned on at both negative and positive electrochemical.[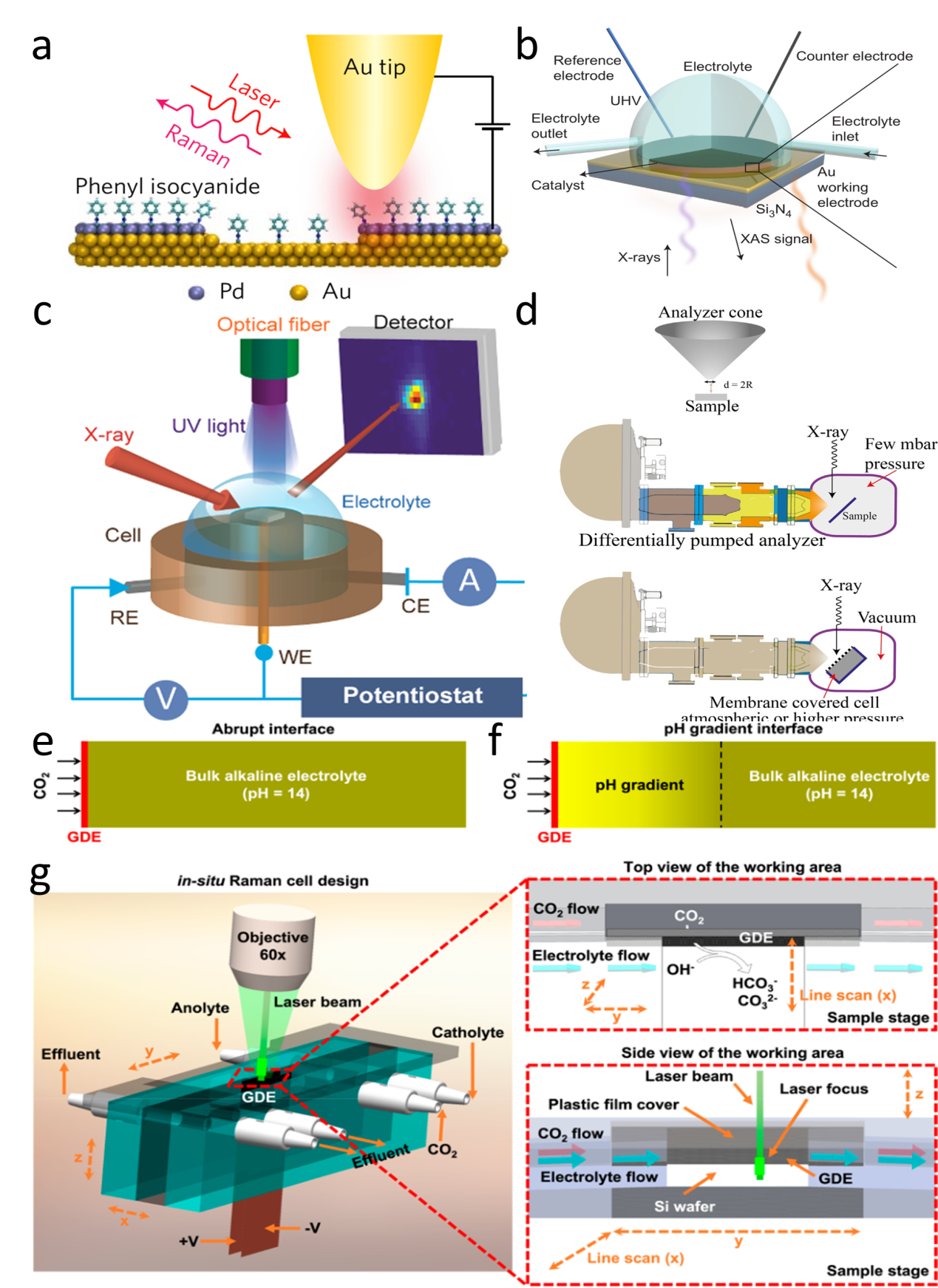 Figure 9. (a) Schematic of an STM-based time-dependent tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS).[
Figure 9. (a) Schematic of an STM-based time-dependent tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS).[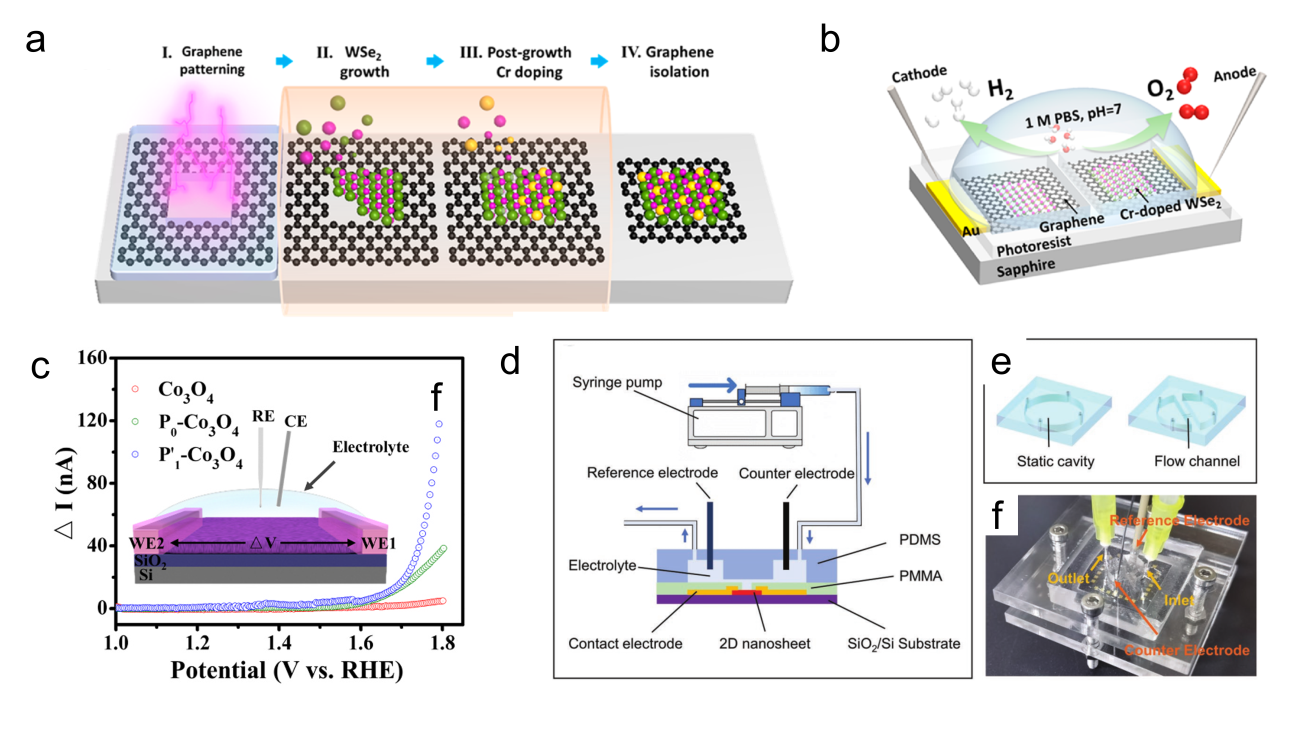 Figure 10. (a) Schematic of the formation process of the Cr-WSe2/graphene heterojunction. (b) Schematic of the on-chip electrocatalytic device.[
Figure 10. (a) Schematic of the formation process of the Cr-WSe2/graphene heterojunction. (b) Schematic of the on-chip electrocatalytic device.[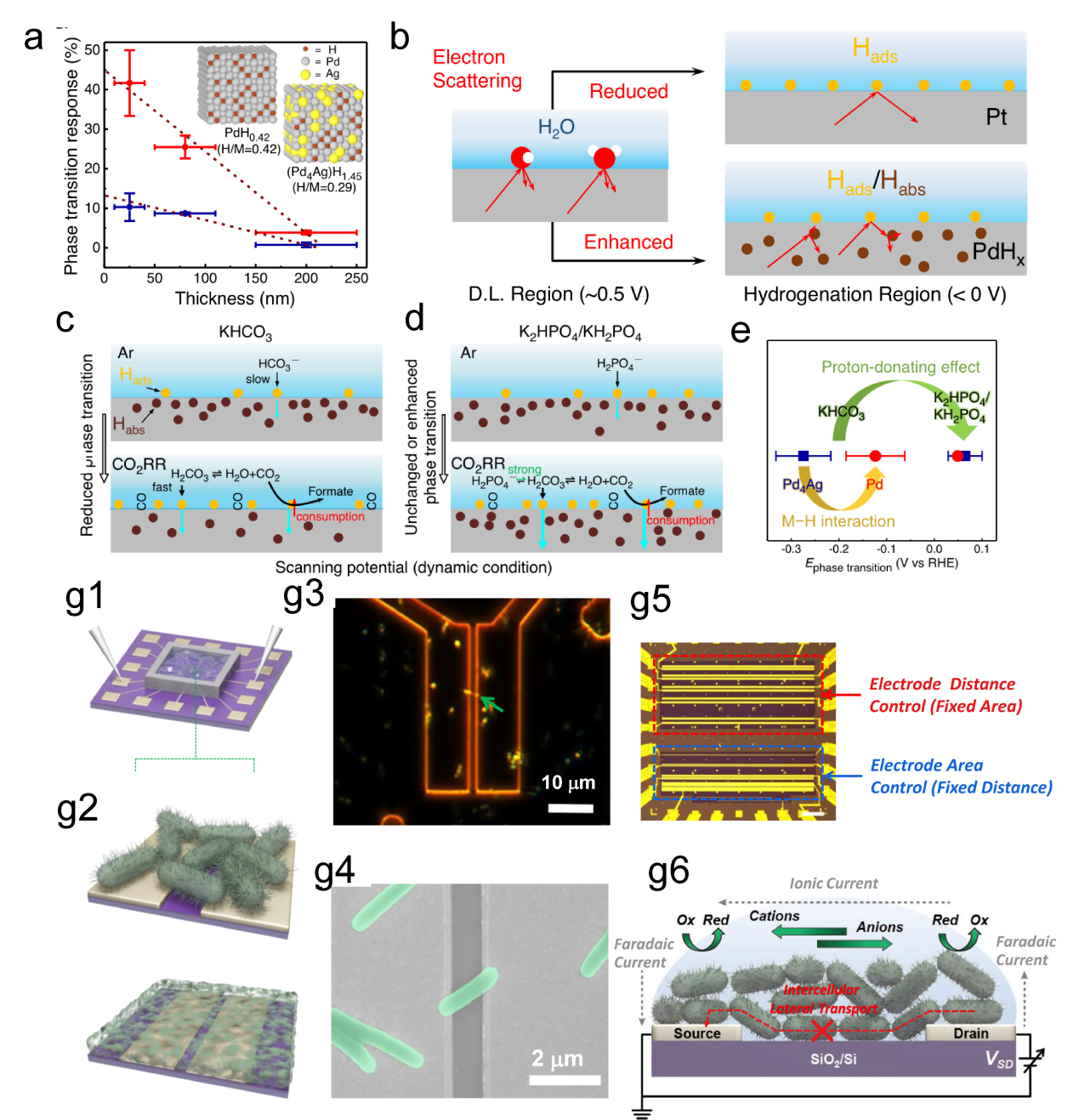 Figure 11. (a) The relationship between the thicknesses of Pd and Pd4Ag nanowire films and their phase transition responses (ΔRMHx) is illustrated on the ETS. (b) Schematic of electron scattering in metals with surface adsorbates and hydrides. A schematic of the different Pd-H states in (c) KHCO3 and (d) K2HPO4/KH2PO4 and the corresponding CO2RR processes at the interfaces. (e) Summary of phase transition potentials of Pd and Pd4Ag under CO2RR conditions in KHCO3 and K2HPO4/KH2PO4 obtained at 10 mV/s.[
Figure 11. (a) The relationship between the thicknesses of Pd and Pd4Ag nanowire films and their phase transition responses (ΔRMHx) is illustrated on the ETS. (b) Schematic of electron scattering in metals with surface adsorbates and hydrides. A schematic of the different Pd-H states in (c) KHCO3 and (d) K2HPO4/KH2PO4 and the corresponding CO2RR processes at the interfaces. (e) Summary of phase transition potentials of Pd and Pd4Ag under CO2RR conditions in KHCO3 and K2HPO4/KH2PO4 obtained at 10 mV/s.[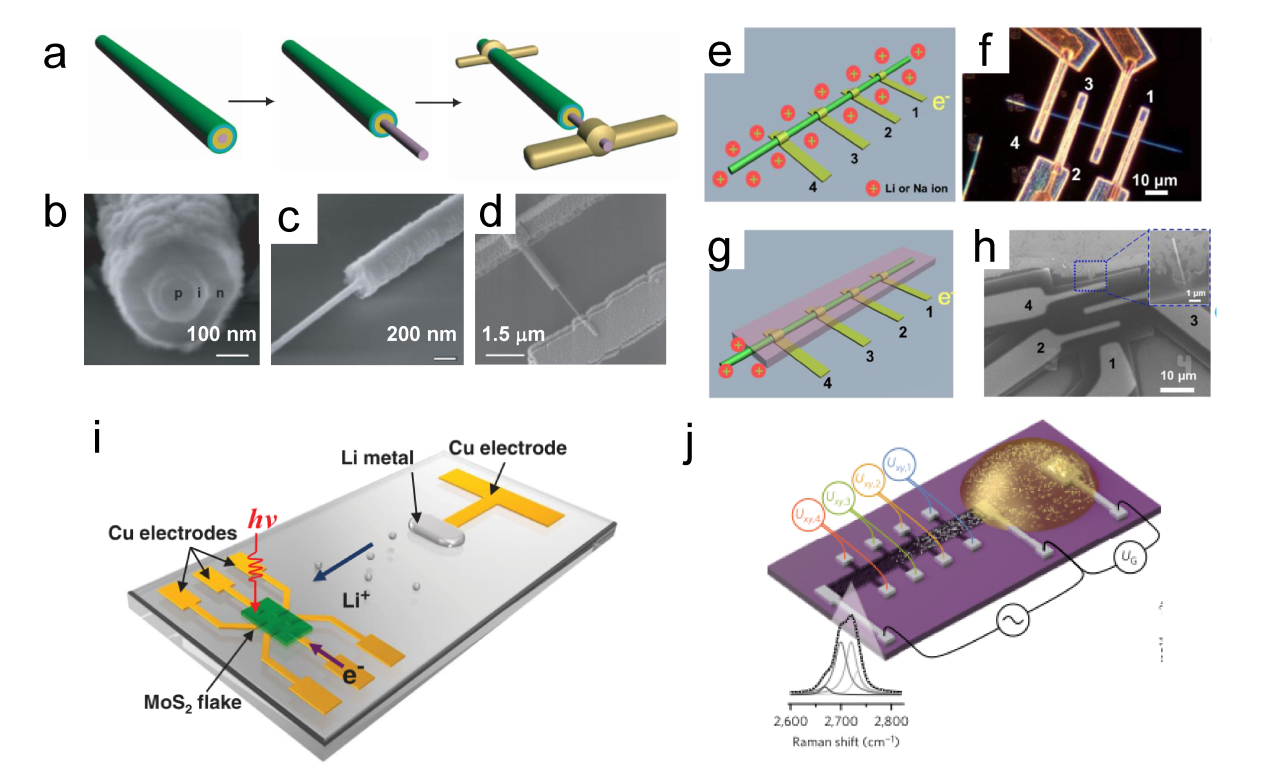 Figure 12. (a) Schematics of fabrication process of the single nanowire photovoltaic device. (b, c, d) SEM images corresponding to schematics in a.[
Figure 12. (a) Schematics of fabrication process of the single nanowire photovoltaic device. (b, c, d) SEM images corresponding to schematics in a.[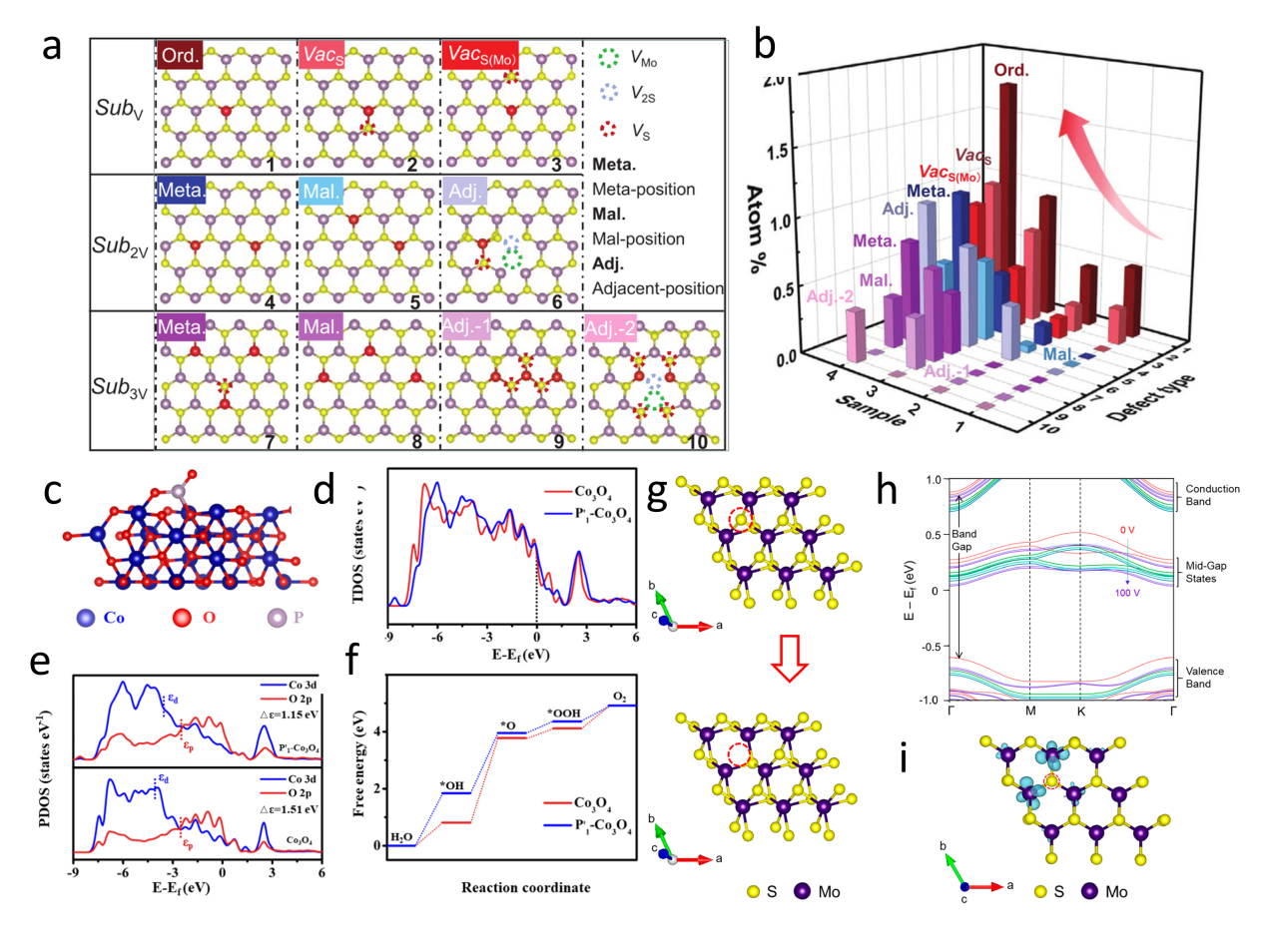 Figure 13. (a) Illustration of atomic defects observed in single-layer V-MoS2. (b) Statistical analysis of the concentration of these atomic defects.[
Figure 13. (a) Illustration of atomic defects observed in single-layer V-MoS2. (b) Statistical analysis of the concentration of these atomic defects.[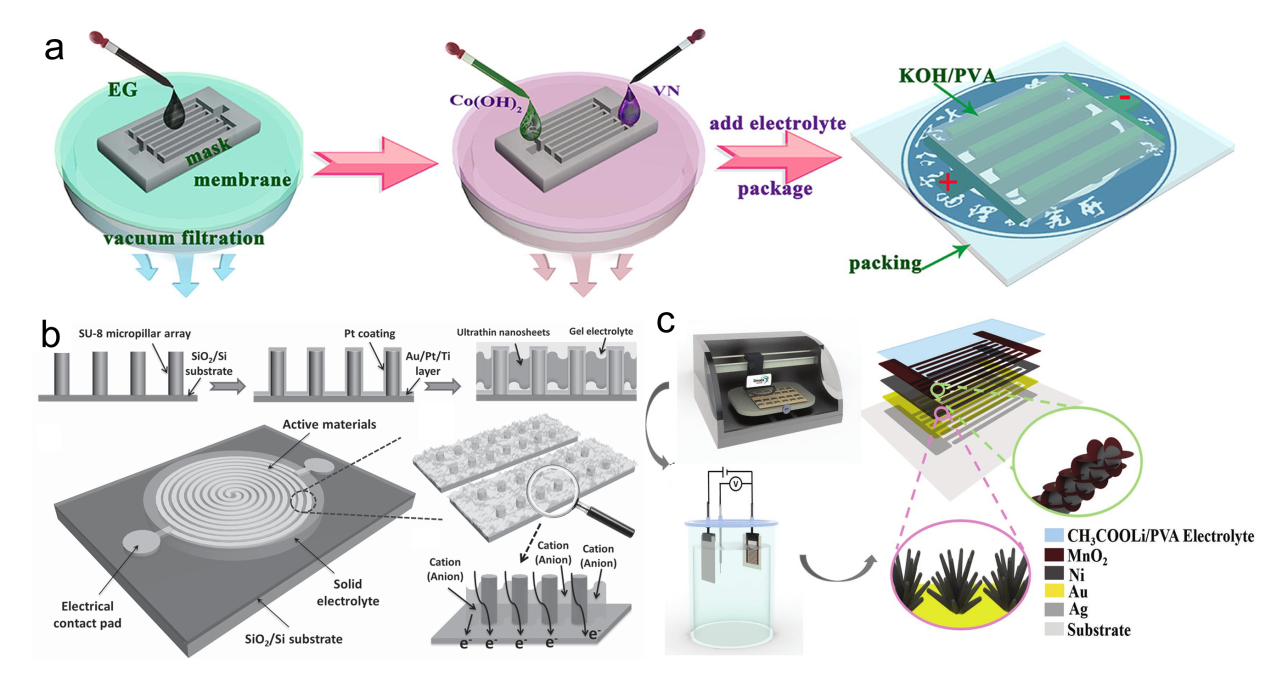 Figure 14. (a) Fabrication and structural characterization of SST-MPCs.[
Figure 14. (a) Fabrication and structural characterization of SST-MPCs.[